Introduction to Hashmap in Java
Hashmap in Java is a part of the Java Collections Framework and allows efficient data retrieval based on a key. Understanding how Hashmap works, its features, and its applications is essential for any Java developer. In this blog, we will dive deep into Hashmap in Java, its internal structure, and the best practices for using it. Additionally, we’ll explore some frequently asked interview questions related to Hashmap.
What is Hashmap in Java?
A Hashmap in Java is a collection that implements the Map interface and stores data in key-value pairs. The key acts as a unique identifier for each value in the map. One of the significant features of a Hashmap is its constant-time complexity (O(1)) for basic operations like insertion, deletion, and retrieval, making it a highly efficient data structure for lookups.
Features of Hashmap in Java
- Key-Value Pair Storage: A Hashmap in Java stores data as key-value pairs, where each key is unique.
- Null Values: Hashmap allows one null key and multiple null values.
- Unordered: Hashmap does not maintain the order of insertion.
- Dynamic Size: The HashMap dynamically increases its size as more elements are added.
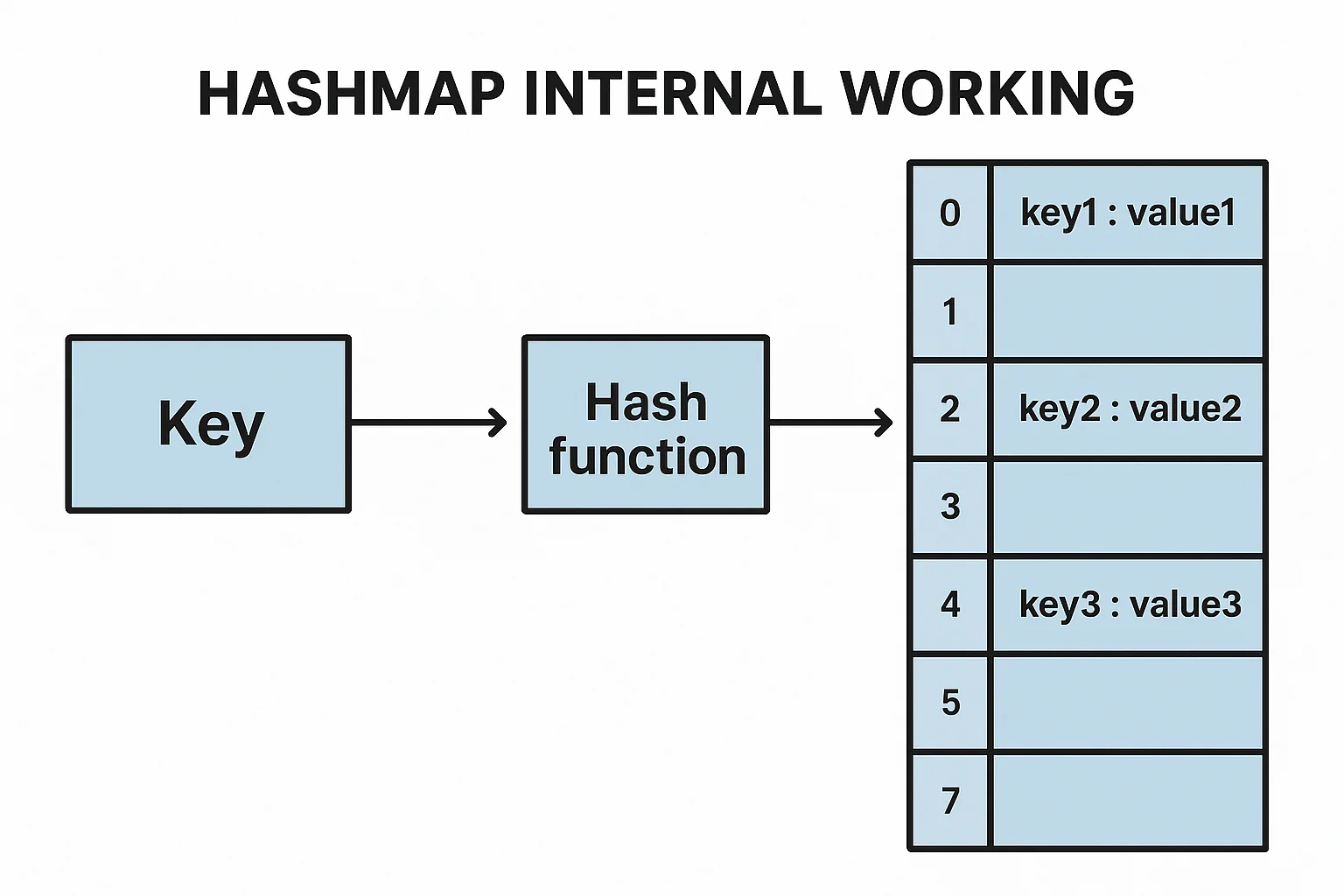
Internal Working of Hashmap in Java
Hashmao contains buckets. When you insert a key-value pair, the key is passed through a hash function that generates a hash code. This hash code determines the bucket where the key-value pair will be stored. If two keys have the same hash code (hash collision), the Hashmap resolves the collision using a technique called chaining (i.e., linked lists).
Each bucket stores a linked list of entries with the same hash code. When retrieving or deleting a value, the Hashmap first calculates the hash code of the key and searches the appropriate bucket. If there are multiple entries in the same bucket (due to collisions), it performs a comparison to find the correct entry.
Advantages of Hashmap
- Fast Retrieval: The main advantage of using a Hashmap in Java is that it provides constant time complexity (O(1)) for basic operations like search, insert, and delete, which is crucial for performance in large applications.
- Dynamic Resizing: The Hashmap resizes automatically when the number of elements exceeds a certain threshold, ensuring it does not run out of space.
- Flexibility: With the ability to store different types of keys and values, Hashmap is very versatile in handling various data structures.
Common Use Cases of Hashmap
- Caching: Developers often use HashMap in caching mechanisms to store previously computed results.
- Database indexing:Developers can use HashMaps to create efficient database indexes..
- Counting occurrences: Hashmap is ideal for counting occurrences of elements in a collection (like words in a text).
Interview Questions on Hashmap
- What is the difference between HashMap and Hashtable in Java?
- HashMap is not synchronized, while Hashtable is synchronized. This makes HashMap faster but not thread-safe, whereas Hashtable is thread-safe but slower.
- How does HashMap handle collisions?
- HashMap uses chaining to handle collisions. If two keys have the same hash code, the system stores the entries in a linked list within the same bucket.
- What happens if you insert a null key in a HashMap?
- HashMap allows only one null key. If you insert a null key, it will successfully store the value for that key.
- What is the time complexity of get() and put() operations in HashMap?
- The time complexity for both
get()andput()operations is O(1), assuming good hash distribution.
- The time complexity for both
- Can developers use HashMap for thread-safe operations?
- By default, HashMap is not thread-safe. If thread safety is needed, consider using
ConcurrentHashMapor synchronizing the access manually.
- By default, HashMap is not thread-safe. If thread safety is needed, consider using
- What is the default initial capacity and load factor of a HashMap in Java?
- The default initial capacity of a HashMap is 16, and the default load factor is 0.75.
- What happens when the load factor exceeds in a HashMap?
- When the load factor exceeds the threshold (capacity * load factor), the HashMap resizes itself, typically doubling its capacity.
- Explain the concept of HashCode in HashMap.
- HashCode is a unique identifier that Java uses to map objects to buckets. A good hash function ensures that HashMap operations are fast and efficient.
Conclusion
The Hashmap is a powerful tool for developers, offering fast and efficient data storage and retrieval. By understanding its inner workings, features, and usage, you can harness its full potential in your Java applications. Whether you’re preparing for an interview or improving your coding skills, mastering Hashmap is crucial for any Java developer.
- How to Use Arrays in Java (with Code Examples for Beginners)
- Compilation in Java – How It Works with Execution Flow, Steps, and Example
- How to Use loops in Java: For, While, Do‑While Explained
- How to Use If Else Statement in Java (With Examples)
- How to Understand Object-Oriented Programming in Java Easily







